وبلاگ
What are Liabilities? Definition, Importance, Types and Examples
If the cost of the accrued expense was estimated, then this adjusting entry will be an estimate. Conversely, if the service period is more than a year, the liability is classified as non-current, or long-term. Contingent Liabilities are possible debts that may happen in the future. These don’t always become real Liabilities, but businesses must still keep track of them. Here’s some answers to commonly asked questions about understanding liabilities in accounting. Next, check out our articles on understanding double declining balance depreciation, how to calculate the current ratio, and 14 common accounting errors and how to avoid adjusting entries them.
Are expenses liabilities or assets?
Higher expenses relative to revenue may indicate inefficiencies or increased costs, while lower expenses may suggest cost-saving measures or improved operational performance. Expenses are subtracted from revenues in the income statement to determine net income. High expenses can decrease profitability, impacting overall financial performance. Bonds payable record debt issued to investors and often carry restrictive covenants that reference the very ratios clean bookkeeping supports. Lease obligations show future payments under long-term operating or https://tivoraclothing.com/2025/12/04/9-best-accounts-payable-software-solutions-in-2025/ finance leases, which can be substantial for facilities or equipment. Operating expenses relate to the core business operations, while non-operating expenses include costs outside typical business activities, such as interest on loans or losses from investments.
What is an Accounting Period?
An expense is a cost that must be incurred by an entity so as to generate business revenue. For example, a manufacturing entity would be required to pay rent to the owner of its factory building and wages to its workers so as to carry on its production activities. Classifying liabilities and expenses correctly isn’t just about accounting hygiene—it shapes how lenders, investors, and decision-makers assess your startup’s financial position. When those entries are off, even slightly, it distorts your ability to manage runway, forecast cash flow, and maintain trust in the numbers. The IRS charges penalties of 2%–15% when those deposits arrive late. Each item touches cash within twelve months, so lenders watch them closely.
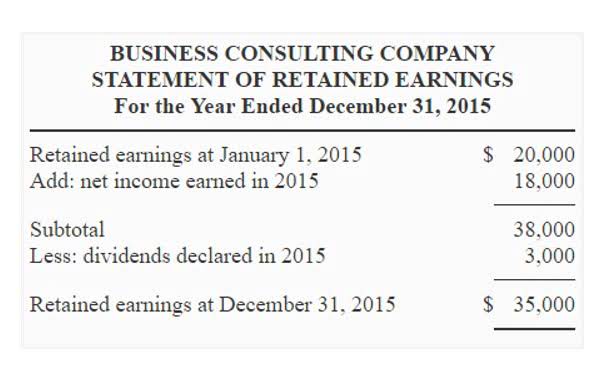
- Non-current liabilities are financial obligations that companies carry on their balance sheets beyond the regular operating cycle or more than one year.
- The balance sheet is one of three financial statements that explain your company’s performance.
- Both liability vs expense result in the cash outflow of funds and are known to be of a similar nature.
- Accrual accounting is a widely used accounting method that records financial transactions as they occur, regardless of when cash is exchanged.
- Being able to distinguish between the two can improve your financial planning and performance for the future.
What are accrued taxes?
While liabilities represent what a company owes, assets represent what it owns or controls, which provides economic value. Assets and liabilities are opposite sides of the balance sheet equation, with assets driving business growth and liabilities often funding that growth. Misclassifying liabilities and expenses creates downstream headaches—inaccurate financial statements, compliance risks, and hours spent hunting are expenses liabilities down errors during audits. You need a system that codes transactions correctly from the start and flags potential issues before they become problems. People often mix them up, but there are key distinctions between liabilities and expenses in accounting, and they’re classified differently in your financial statements. The timing of recognition is another separating factor under the accrual method of accounting.
- These are usually due more than a year from now, but they still need to be tracked so clients can plan ahead.
- With liabilities booked cleanly, the next step is understanding how to treat expenses—especially when they’re recurring, direct, or non-operating.
- That’s because the cost was incurred during the period but was never included in the reported expenses.
- Properly recording both categories ensures error-free financial statements and reports, facilitating effective financial planning.
- They would continue to do so each month until the services were no longer in use.
Understanding the differences between liabilities and expenses is essential for accurate financial reporting, strategic planning, and compliance with accounting standards. This article explores the key disparities between liabilities and expenses, their classification, impact on financial statements, and the importance of proper accounting practices for each. When it comes to financial accounting, understanding the difference between expenses and liabilities is crucial. Both terms are commonly used in financial statements, but they represent different aspects of a company’s financial obligations. In this article, we will explore the attributes of expenses and liabilities, highlighting their definitions, characteristics, and how they impact a company’s financial health.
The impact of expenses on the balance sheet

This is because accruals represent expenses that have been incurred but not yet paid, which reduces the amount of income that is recognized in the period. Accrued expenses are recorded in the income statement as an expense, but they are also recorded in the balance sheet as a current liability. This is because the company owes payment for the services or goods that have been received. Upon payment of the accrued liability, the company will make another journal entry to reverse the initial accrual. This entry involves debiting the liability account and crediting the cash or bank account. This process ensures that the liability is removed from the books once the expense has been paid, maintaining accurate financial records.


Entities reporting under US GAAP are required to use the accrual basis of accounting. In other words, businesses using the accrual basis should recognize expenses for goods and services they have received when they use them even if they have not paid for them. Accrued liabilities are expenses your business owes that have been incurred but not yet invoiced for or paid. Accrued liabilities are recorded as current liabilities if they are expected to be settled within a year. Current liabilities are debts or obligations that your business must settle within the next 12 months. These are short-term liabilities that help you manage the day-to-day financial obligations of your business.
